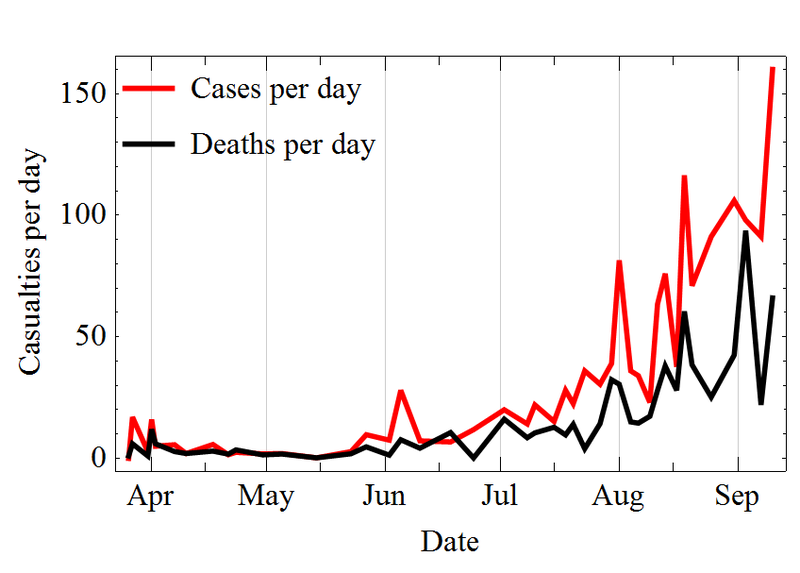
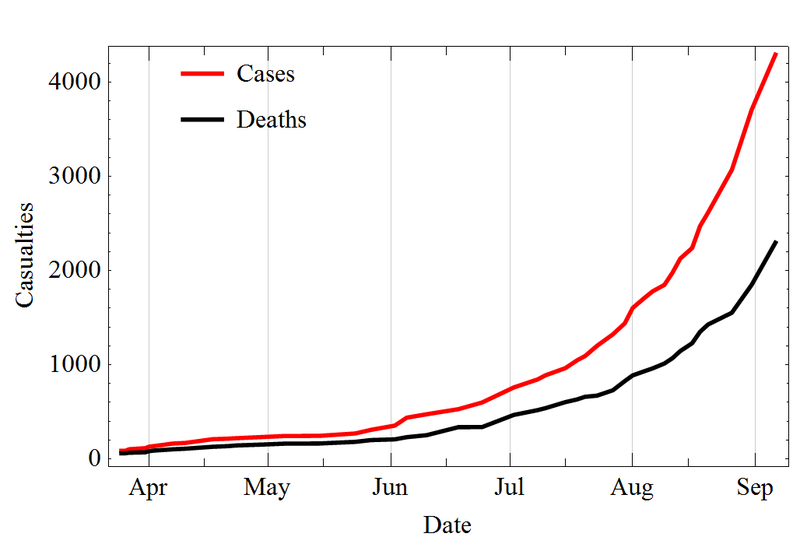
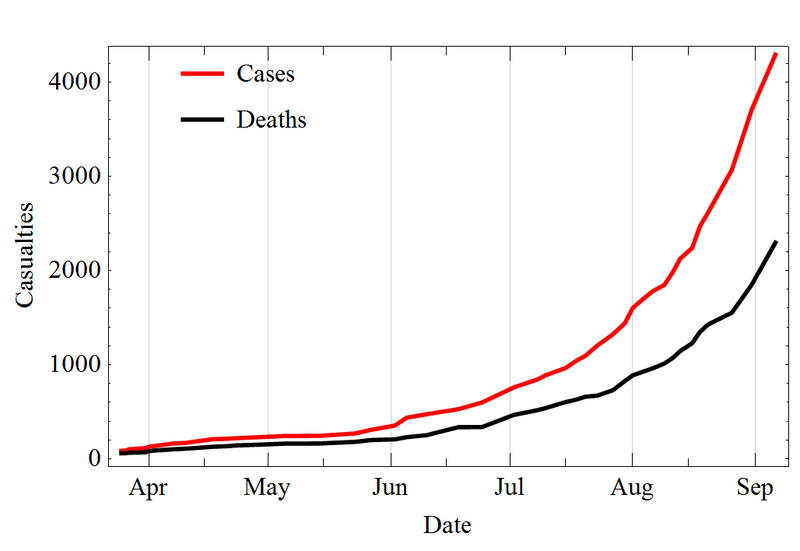
Ebola Deaths
Ebola Cases Now Above 15,000 WHO Says
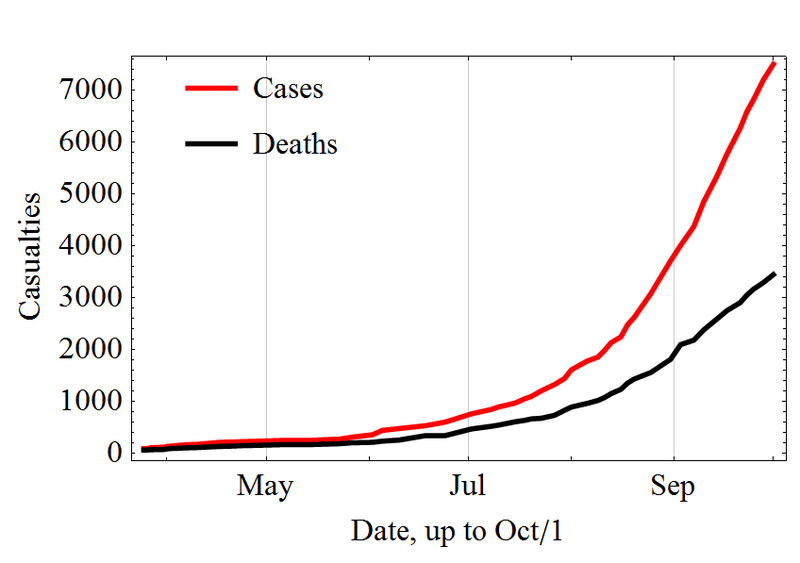
The outbreak of the Ebola virus in West Africa reached 15,351 cases in what is the worst oubreak of the disease in history, new figures from the World Health Organisation show on Friday. There have also been 5,459 reported deaths linked to the virus, including nearly 3,000 in Liberia alone, according to the latest figures from the WHO. Liberia, along with Guinea and Sierra Leone, have been hardest hit by the outbreak, accounting for almost all the cases and fatalities.
The number of Ebola cases rise sharply in Sierra Leone
The number of new cases of Ebola in Sierra Leone has jumped dramatically, putting paid to any hopes that the infection rate is slowing. Official figures released by the minister of health and sanitation show there were 111 new cases registered on Sunday, the highest daily rate since the ministry started publishing figures in August. There were 45 new cases the day before, including 24 in the capital, Freetown.
Reported Ebola cases jump 30 percent in just four days
The World Health Organization says the number of reported Ebola cases has surpassed 13,700, a jump of more than 30% since the last numbers were released four days ago. Dr. Bruce Aylward, assistant director-general of the WHO, said the big increase in cases is likely because of previous under-reporting.
There are now more than 10,000 Ebola cases in eight countries
The number of people infected with the Ebola virus has passed 10,000, with 4992 deaths, according to the World Health Organisation, as the United States announced its ambassador to the United Nations would visit the three worst-affected West African nations. It says 10,141 people have been diagnosed with the deadly disease, which is an increase from the previous estimate of about nine thousand cases. Almost five thousand people have died from the virus, which has hit Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone the hardest.
Ebola Death Toll Could Actually Be Three Times Higher Than Reported
At least 4,877 people have died in the world’s worst recorded outbreak of Ebola as of Oct. 19, the World Health Organization (WHO) said on Wednesday, but the true toll may be three times as much. At least 9,936 cases of the disease had been recorded, according to the WHO, but the actual numbers may be three times higher.
U.S. General: ‘By the end of the year, there’s supposed to be 1.4 million people infected with Ebola and 62 percent of them dying’
The potential spread of Ebola into Central and Southern America is a real possibility, the commander of U.S. Southern Command told an audience at the National Defense University here yesterday.
82 percent of Ebola patients are being turned away from hospitals to die at home, spreading infections to family members
A lack of available hospital beds in Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea, the three countries at the epicenter of the worst Ebola outbreak in history, is leaving many families with nowhere to take their sick and dying. More than 80 percent of Ebola patients, in fact, are being turned away from hospitals and sent back home, where they continue to spread the disease to family members, friends and others in the community. A major shortage of beds and healthcare workers throughout the region has created an every-man-for-himself situation in which infected folks are having to basically fend for themselves.
The Pure Hell At The Heart Of The Ebola Pandemic In Africa Could Soon Be Coming To America
Did you know that the number of Ebola cases in Liberia and Sierra Leone is approximately doubling every 20 days? People are dropping dead in the streets, large numbers of bodies are being dumped into the rivers, and gravediggers can hardly keep up with the the number of corpses that are being delivered to the cemeteries. As you read this, life is pure hell in many areas of West Africa, and now the CDC is warning that things may get far, far worse in the very near future.
Exponential: Ebola Cases Now Double Every 3 Weeks; CDC Warns As Many As Half A Million May Be Infected Soon
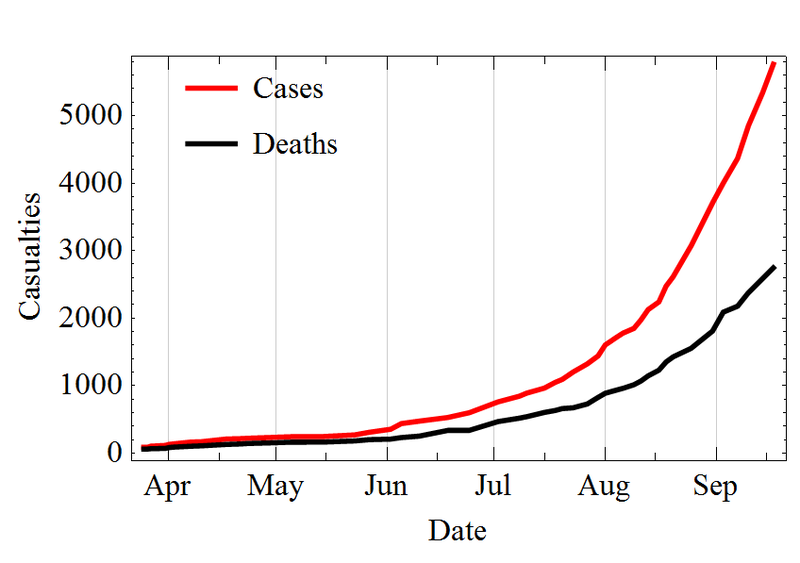
Since the start of the outbreak, the Ebola virus has infected 5,357 people, killing 2,630, according to the WHO; and as The UN explains, the outbreak is the largest the world has ever seen with the number of cases is doubling every three weeks. As Sierra Leone instigates a 3-day nationwide shutdown to contain the deadly virus, the UN Secretary-General explains “Ebola matters to us all,” as we noted previously the odds of the infection coming to America is around 18% by year-end. The CDC, however, hot on the heels of the UN’s proclamation that “the gravity and scale of the situation now require an unprecedented level of international action,” has warned that unless government intervention is increased significantly, 550,000 people could be infected by the end of January.
Is It Wise For Obama To Send Thousands Of U.S. Troops Into The Ebola Death Zone?
When there is a major problem somewhere in the world, Barack Obama loves to show that he is “doing something” by sending a contingent of U.S. troops to the affected area.
Worst-ever Ebola outbreak, by the numbers
Number of countries with cases: 5 (Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Nigeria, Senegal) Number of cases as of Sept. 16:
Ebola cases double in Congo – 35 dead, nearly 400 people may be infected
The number of Ebola cases in the Democratic Republic of Congo doubled over the past week to 62, the World Health Organization reported Thursday, and more than half the afflicted patients have died. The outbreak in the country, where the Ebola virus was first discovered nearly 40 years ago, is a distinct strain from the far more drastic Ebola crisis ravaging West Africa, where more than 2,200 people have died this year, the worst on record. The Congo outbreak, by contrast, is confined to four villages in one county, and is linked to one initial case, first reported to the health organization on Aug.
How deadly is Ebola? Statistical challenges may be inflating survival rate
The Ebola virus that is causing the raging epidemic in West Africa is famously lethal. In previous outbreaks it has killed as many as 90% of the people it infects. That’s why the figures in World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) latest “Situation Report” look like they might be a rare glimmer of good news.
Scientific Model: 1.2 Million Will Be Dead From Ebola In 6 Months
An econometric simulation model based on the assumption the World Health Organization and others will be unable to control the Ebola outbreak in West Africa predicts 1.2 million people will die from the disease in the next six months. Six months is the minimum time the WHO projects will be necessary to contain the epidemic.
No More Places To Put Ebola Patients In Liberia But Cases Are Growing Exponentially
There is not a single empty bed available for an Ebola patient in Liberia right now, but thousands more cases are expected in the coming weeks. Entire families have been driving around in taxis looking for some place that will take their sick family members, but every treatment facility is already full. According to the World Health Organization, many of those potential Ebola patients end up returning to their homes where there will inevitably spread the virus to even more people.